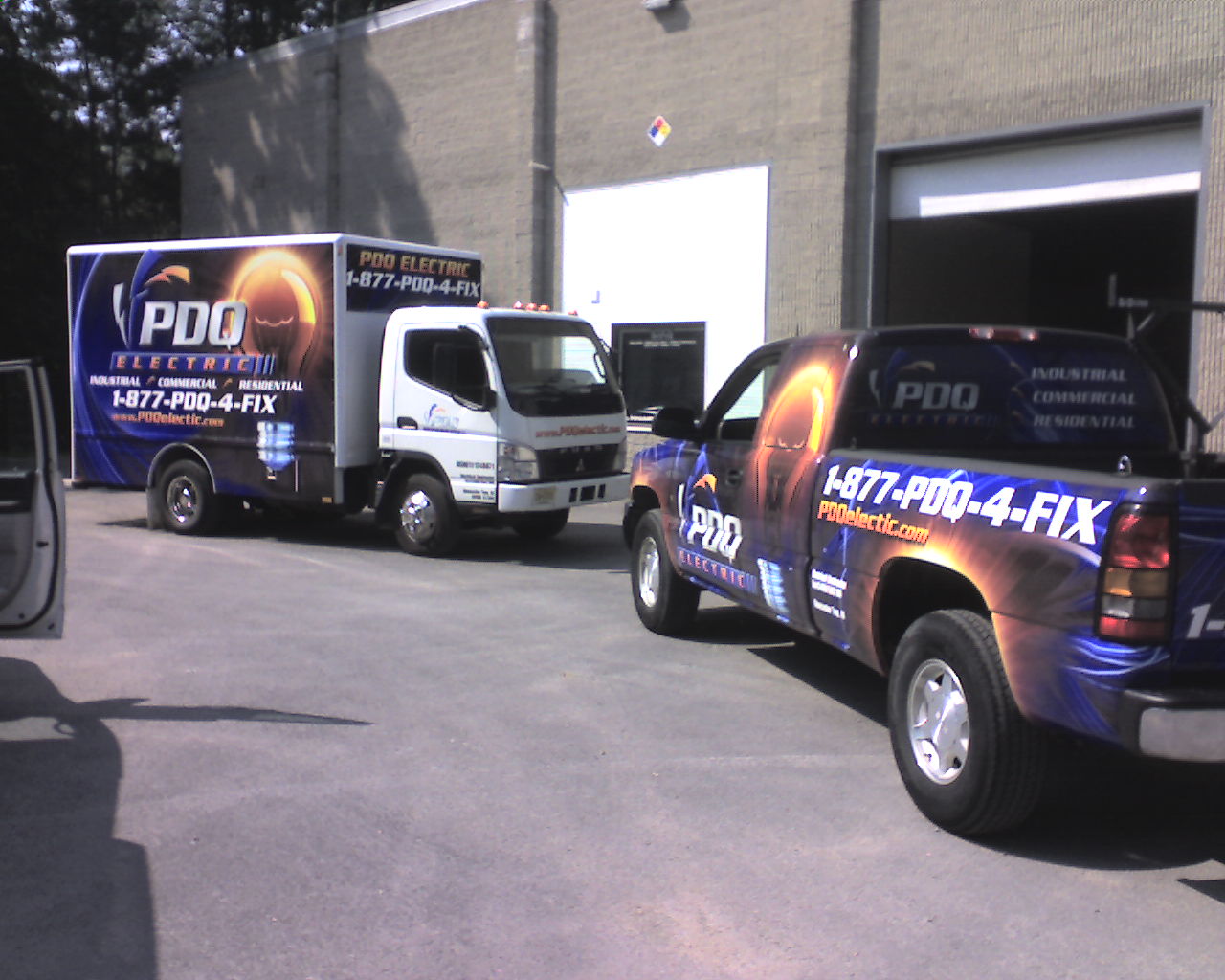
 Industrial - Commercial
Industrial - Commercial  Electrical
Contractor
Electrical
Contractor 
PDQ Electric Corp
NJ, PA, DE, MD, NY, CT, DC, MA, RI
|
PDQIE - PDQ Industrial ElectricQuality Control SystemsQuality control is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:
Six SigmaSix Sigma is a disciplined, data-driven approach and methodology for eliminating defects (driving towards six standard deviations between the mean and the nearest specification limit) in any process - from manufacturing to transactional and from product to service. The statistical representation of Six Sigma describes quantitatively how a process is performing. To achieve Six Sigma, a process must not produce more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities. A Six Sigma defect is defined as anything outside of customer specifications. A Six Sigma opportunity is then the total quantity of chances for a defect. There are various frameworks for implementing the Six Sigma methodology. Six Sigma Consultants worldwide have developed proprietary methodologies for implementing Six Sigma quality, based on the similar change management philosophies and application of tools. The fundamental objective of the Six Sigma methodology is the implementation of a measurement-based strategy that focuses on process improvement and variation reduction through the application of Six Sigma improvement projects. In other words, Six Sigma strives to eliminate defects and improve quality through repeatable measurable processes. This is accomplished through the use of two Six Sigma sub-methodologies: DMAIC and DMADV. The Six Sigma DMAIC process (define, measure, analyze, improve, control) is an improvement system for existing processes falling below specification and looking for incremental improvement. The Six Sigma DMADV process (define, measure, analyze, design, verify) is an improvement system used to develop new processes or products at Six Sigma quality levels. It can also be employed if a current process requires more than just incremental improvement. Both Six Sigma processes are executed by Six Sigma Green Belts and Six Sigma Black Belts, and are overseen by Six Sigma Master Black Belts. The key concepts of Six Sigma are Critical to Quality (attributes most important to the customer), Defect (failing to deliver what the customer wants), Process Capability (what your process can deliver), Variation (what the customer sees and feels), Stable Operations (ensuring consistent and predictable processes to improve what the customer sees and feels) and Design for Six Sigma (designing to meet customer needs and process capability). Processes become more capable when they are standardized across the organization and their performance is monitored against historical data. This way you can detect variation in performance early enough to address it less expensively. And ultimately, the process should be continuously improving through identifying the root causes of variability and innovative ways to fulfill its objectives. | |
(877) 737-4349 (Toll Free)
(877) PDQ-4-FIX (Toll
Free)
(856) 625-6969 (Text
Messaging)
PDQ ia an Acronym for "Pretty Damn Quick"
|
PDQIE, www.PDQIE.com, info@PDQIE.com, quote@PDQIE.com, Ryan@PDQIE.com, PDQ Industrial Electric, www.PDQIndustrialElectric.com, info@PDQIndustrialElectric.com, quote@PDQIndustrialElectric.com, Ryan@PDQIndustrialElectric.com are marketing tools of PDQ Electric Corp, a NJ Licensed Electrical Contractor. Reddy Kilowatt® is a Registered Trademark of Northern States Power Company. The information on this website is believed to be reliable, but we cannot guarantee that information will be accurate, complete and current at all times and should be reaffirmed by a licensed professional before relying on it. PDQIE will from time to time revise information, products and services described in-on this Website, and reserves the right to make such changes without notice. Use of this Website is entirely at your risk. Materials and information in this Website (including text, graphics, and functionality) are presented without express or implied warranties of any kind and are provided "as is". It is your responsibility to evaluate the accuracy, completeness and usefulness of any opinions, advice, services and information provided.